How Tissue Culture is Revolutionizing Agriculture
The Future of Farming: How Tissue Culture is Revolutionizing Agriculture
Tissue culture in agriculture is emerging as a transformative force in modern farming. While it has gained attention in specialized industries like cannabis cultivation, its applications extend far beyond niche markets. By creating disease-resistant crops, boosting agricultural yields, and supporting sustainable farming techniques, tissue culture is reshaping the way we grow food and manage resources.
What is Tissue Culture in Agriculture?
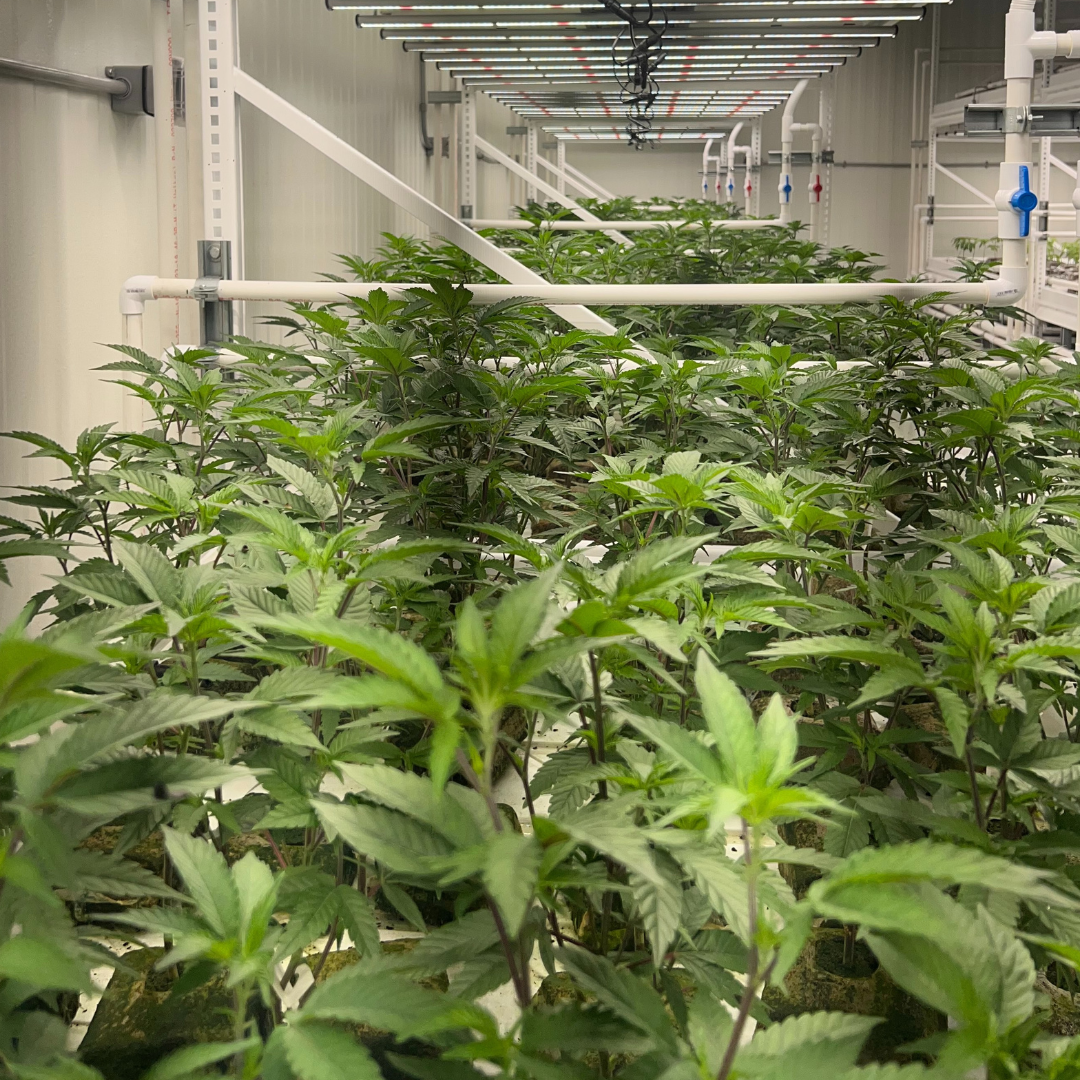
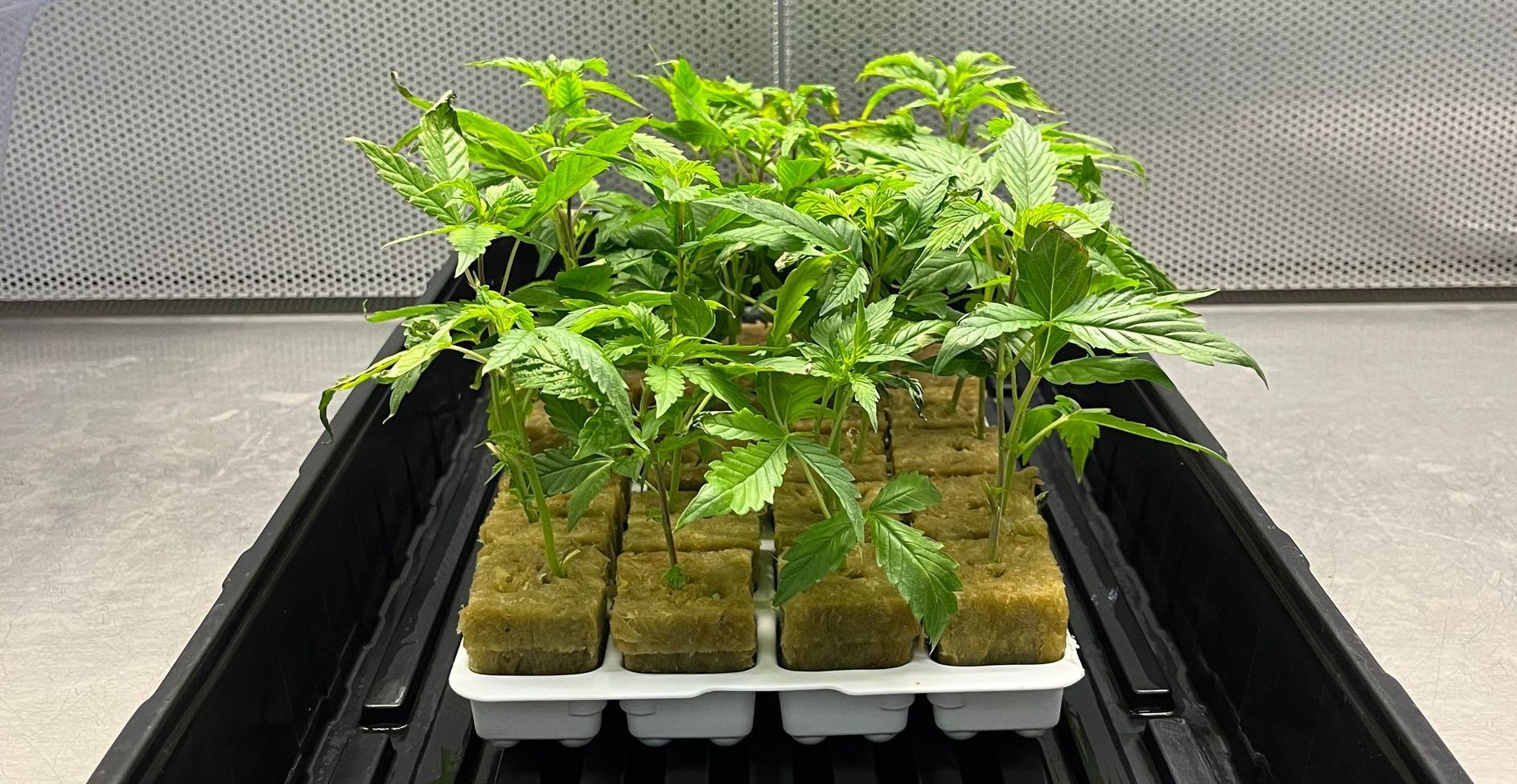
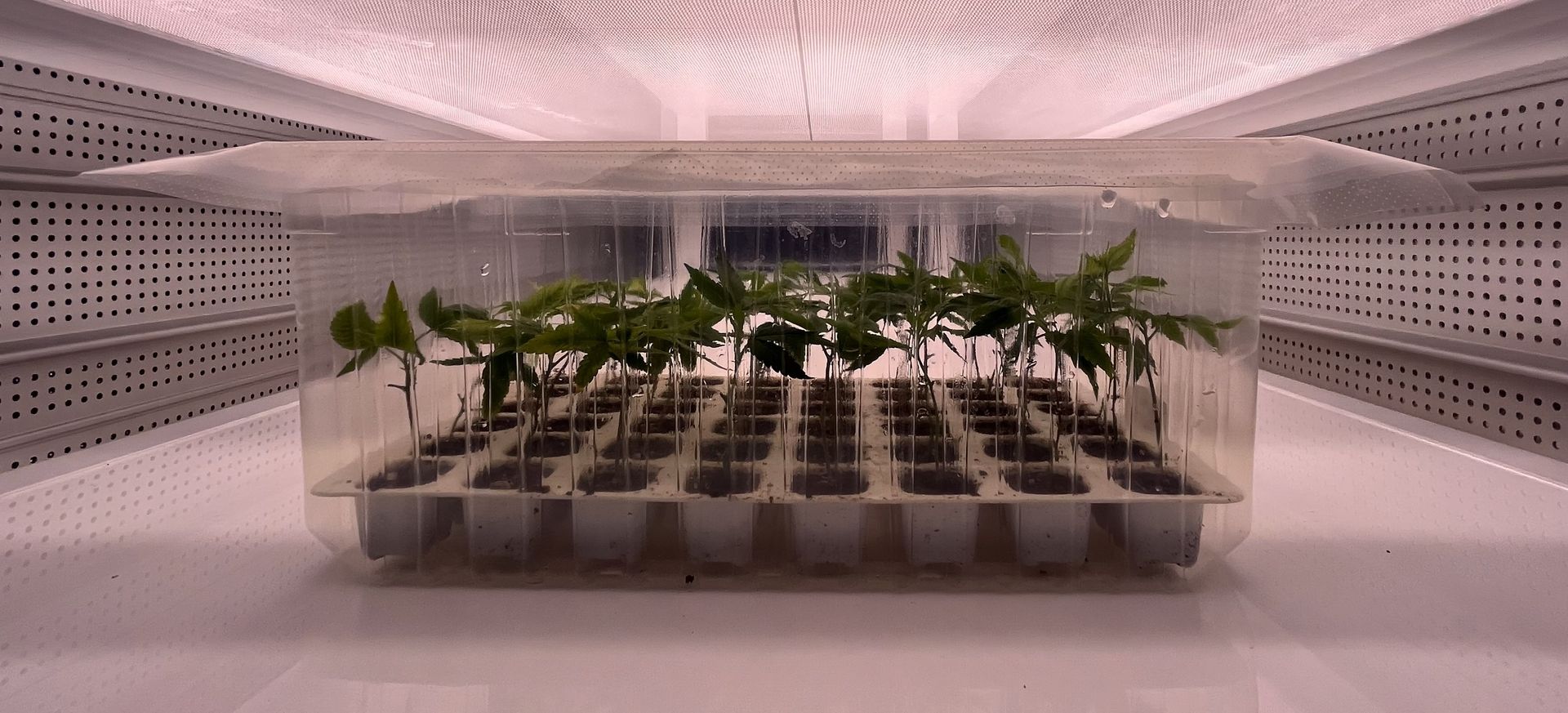
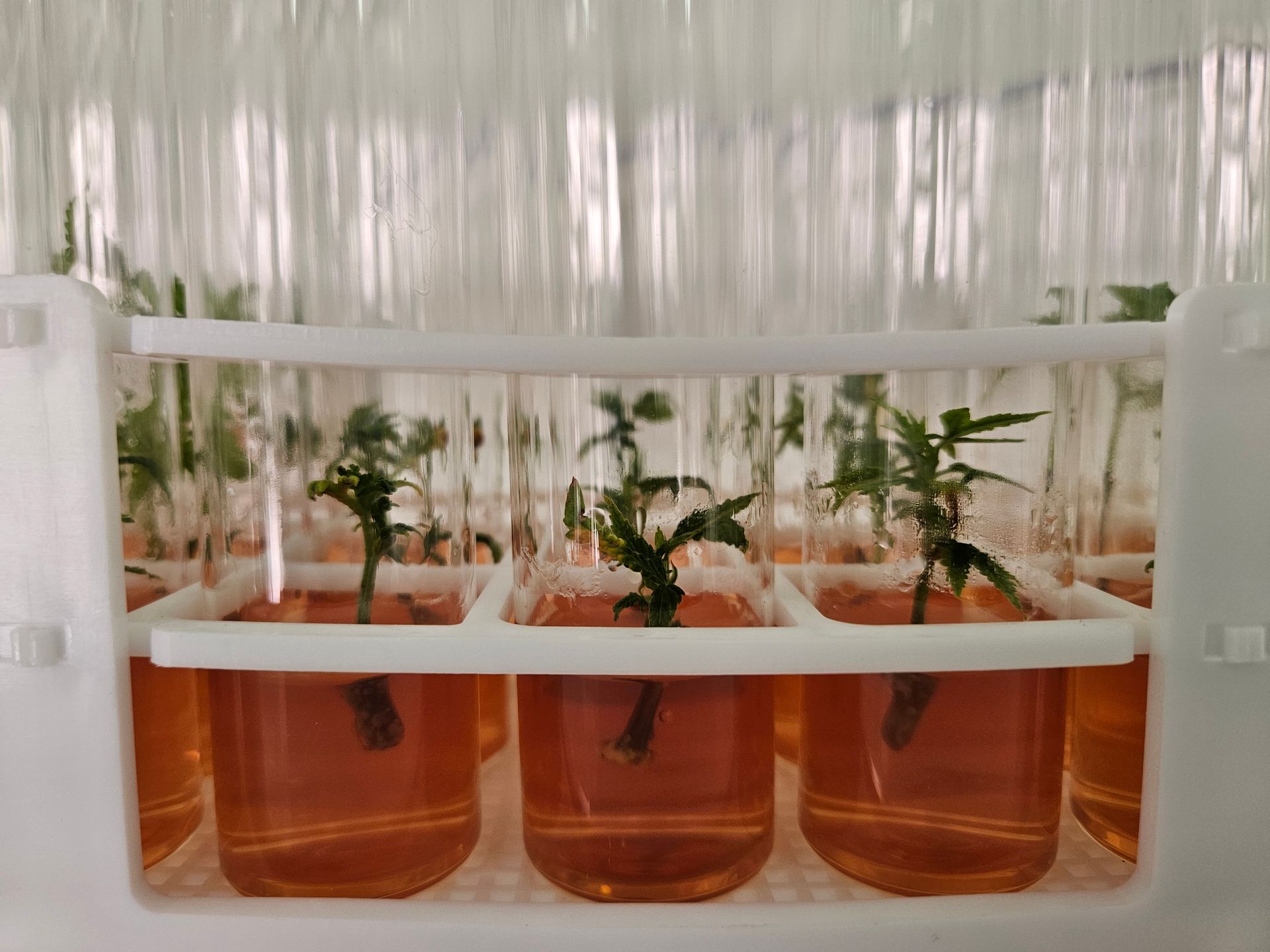
At its core, tissue culture involves growing plants from small samples of cells or tissues in a controlled, sterile environment. These lab-grown plants are identical to their parent plants, ensuring consistent quality and traits. This precision has profound implications for agricultural biotechnology, making it possible to cultivate plants that are more resilient, productive, and adaptable to changing climates.
How Tissue Culture Increases Agricultural Yields
Traditional farming often struggles with inconsistencies in crop quality and yield due to factors like pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. Tissue culture addresses these challenges by:
- Producing Uniform Crops: Each plant grown through tissue culture is a genetic clone, ensuring uniformity in size, taste, and quality.
- Accelerating Growth Cycles: Tissue-cultured plants often grow faster, allowing farmers to maximize their harvests.
- Scaling Up Production: Farmers can propagate large quantities of high-performing plants from a single parent, meeting demand efficiently.
These advantages make tissue culture an invaluable tool for increasing food production in a world facing rapid population growth.
Disease-Resistant Crops for a Healthier Future
One of the most significant contributions of tissue culture is the development of disease-resistant crops. Plants grown in sterile lab environments are free from pathogens and pests that commonly plague traditional farming. This technique also enables researchers to focus on breeding crops with natural resistance to specific diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and fertilizers.
For example, banana farming has benefited immensely from tissue culture. By propagating disease-resistant banana plants, the industry has been able to combat threats like Panama disease, which devastates traditional plantations.
Tissue Culture and Sustainable Farming Techniques
As global agriculture faces increasing pressure to adopt eco-friendly practices, tissue culture offers a path to sustainability:
- Reducing Land Use: Tissue culture allows for higher yields on smaller plots of land, preserving natural ecosystems.
- Minimizing Chemical Inputs: Disease-resistant plants reduce reliance on harmful pesticides and fertilizers, improving soil and water quality.
- Conserving Resources: With more efficient growth and fewer losses, tissue culture helps farmers use resources like water and energy more responsibly.
These innovations align with the goals of sustainable farming techniques, making tissue culture a vital tool in combating climate change and ensuring food security.
Broader Applications in Agricultural Biotechnology
Tissue culture is not limited to staple crops. It has applications in preserving endangered plant species, developing ornamental plants for horticulture, and even growing plants in urban or vertical farming systems. Its versatility makes it a cornerstone of agricultural biotechnology, opening new avenues for innovation in farming.
Why Tissue Culture Matters Beyond Cannabis
Although tissue culture is widely recognized in the cannabis industry, its potential impact on global agriculture is far more significant. Farmers of all scales, from smallholders to industrial operations, stand to benefit. Additionally, sustainability advocates and biotech enthusiasts see tissue culture as a revolutionary step toward more resilient and environmentally conscious food systems.
Conclusion
The future of farming is here, and tissue culture in agriculture is leading the charge. By enabling sustainable farming techniques, increasing yields, and fostering the development of disease-resistant crops, tissue culture addresses some of the most pressing challenges in modern agriculture. As the technology continues to evolve, its applications will only expand, offering a brighter, more sustainable future for farmers and consumers alike.
With its ability to drive progress and innovation, tissue culture is not just revolutionizing agriculture—it’s ensuring a healthier, more sustainable planet.










